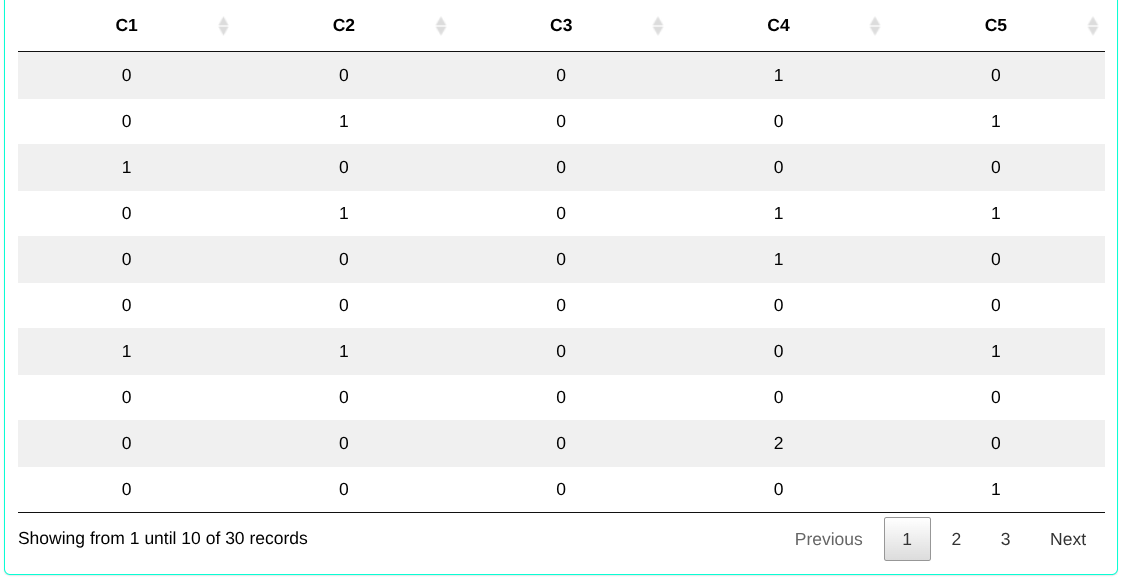
14. Generate random numbers
The Generate Random Numbers tool allows you to generate random samples of diverse continuous and discrete distributions.
Example 1:
Consider X a Normal random variable with mean 11.15 and Standard Deviation 2.75. Generate two random samples of size 50.
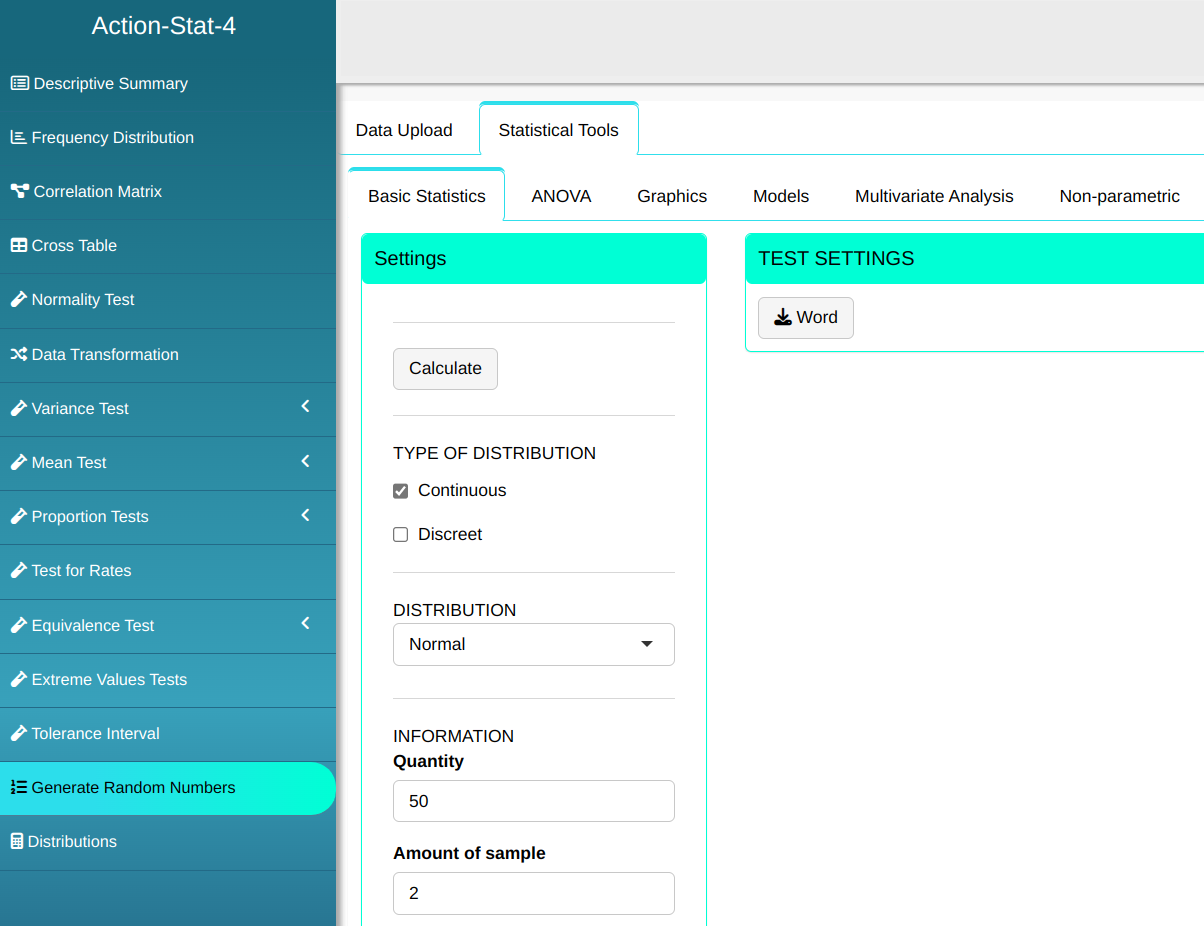
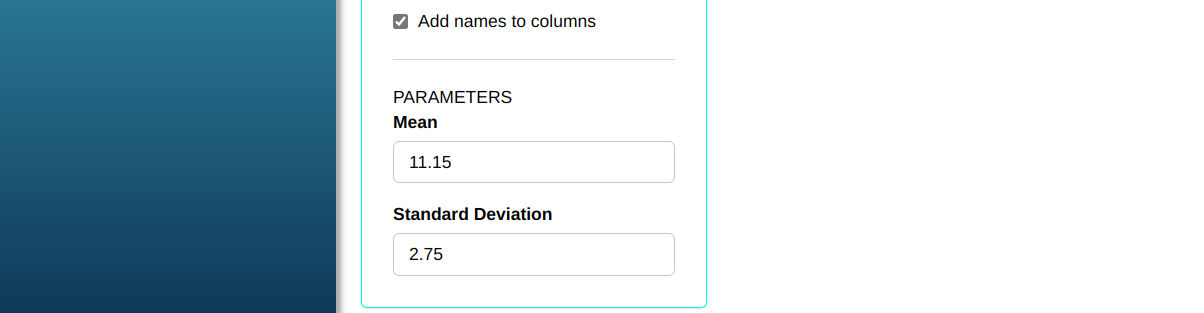
Then click Calculate to get the results. You can also generate the analyses and download them in Word format.

The results are as follows:
| C1 | C2 |
|---|---|
| 14.519 | 6.768 |
| 13.603 | 9.302 |
| 10.583 | 7.906 |
| 10.055 | 4.139 |
| 16.292 | 12.949 |
| 13.104 | 6.290 |
| 8.016 | 10.154 |
| 13.028 | 12.093 |
| 12.468 | 7.728 |
| 14.554 | 13.992 |
| 11.572 | 13.555 |
| 10.333 | 14.062 |
| 14.448 | 9.877 |
| 9.898 | 11.983 |
| 14.173 | 13.896 |
| 10.658 | 14.588 |
| 11.824 | 13.786 |
| 13.990 | 9.173 |
| 12.317 | 12.660 |
| 10.655 | 9.766 |
| 8.303 | 15.435 |
| 9.175 | 10.997 |
| 10.330 | 8.585 |
| 7.750 | 8.318 |
| 9.505 | 9.416 |
| 11.414 | 6.462 |
| 10.690 | 9.933 |
| 9.248 | 11.784 |
| 9.409 | 6.800 |
| 7.104 | 8.107 |
| 9.037 | 10.435 |
| 7.988 | 7.878 |
| 13.855 | 7.882 |
| 5.254 | 8.999 |
| 16.544 | 12.134 |
| 11.047 | 12.970 |
| 7.360 | 10.156 |
| 7.047 | 8.676 |
| 9.138 | 10.520 |
| 10.802 | 8.213 |
| 10.807 | 13.239 |
| 10.400 | 14.622 |
| 5.942 | 15.262 |
| 12.231 | 12.857 |
| 12.549 | 14.257 |
| 16.099 | 17.609 |
| 9.344 | 9.701 |
| 1.816 | 12.335 |
| 7.253 | 10.463 |
| 14.306 | 7.440 |
Example 2:
Generate a random sample of size 10000 from the distribution Exponential, with parameter lambda = 0.01
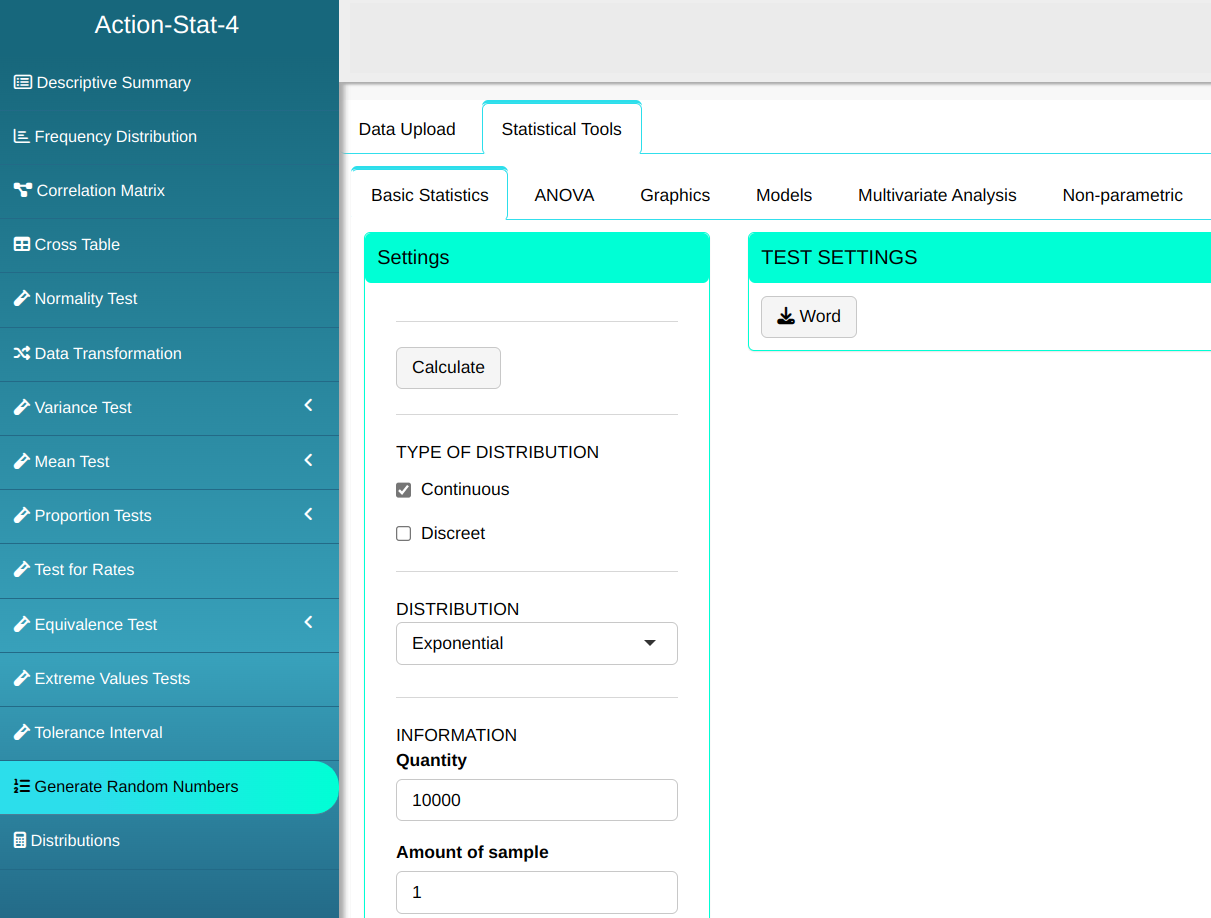
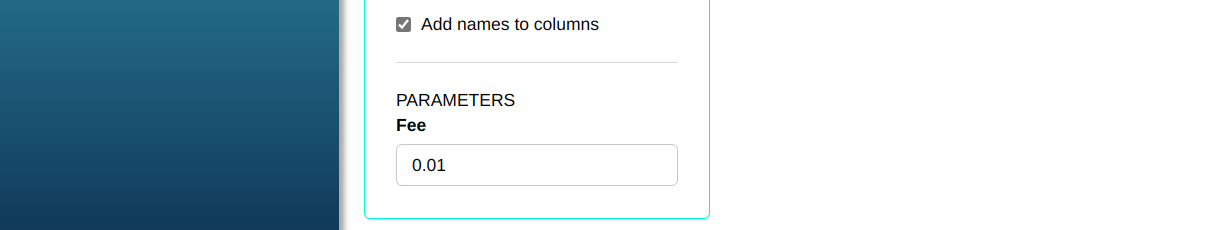
Then click Calculate to get the results. You can also generate the analyses and download them in Word format.

The results are as follows:
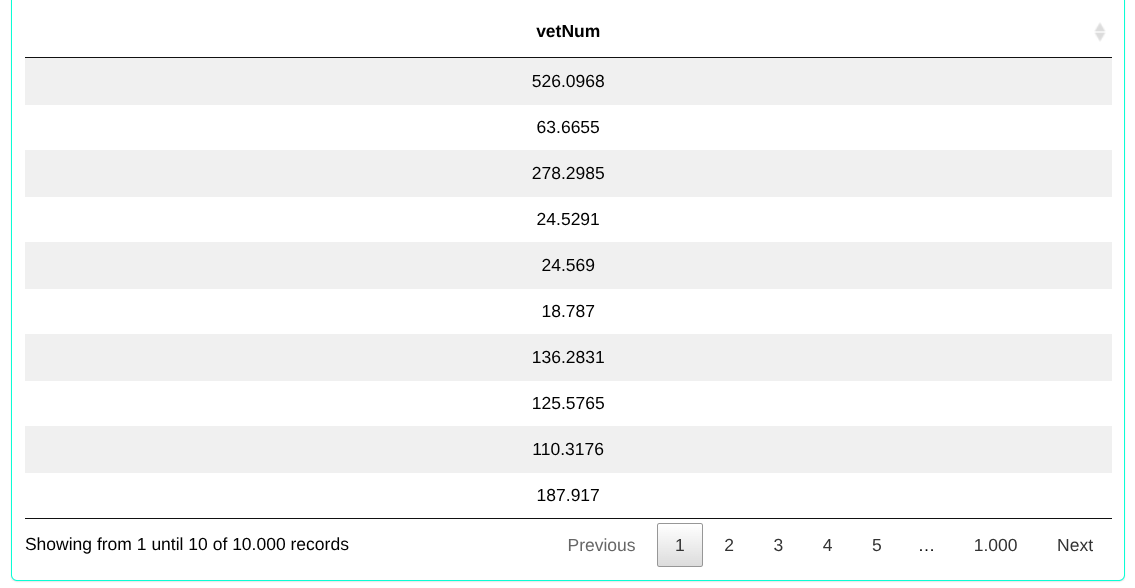
Example 3:
Consider a random variable X with a binomial distribution with parameters n = 30, k = 1 and prob = 0.1. Determine the random sample from the binomial distribution.
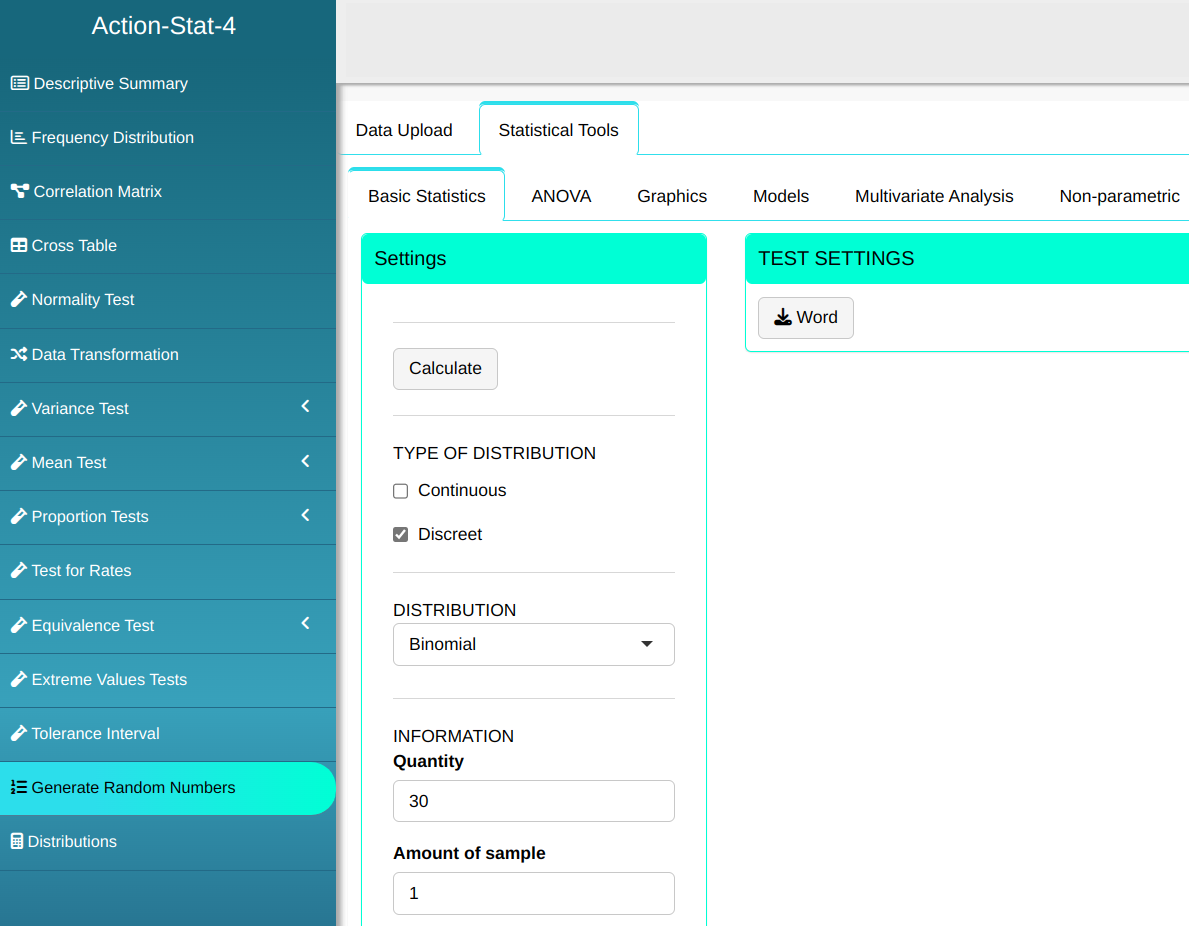
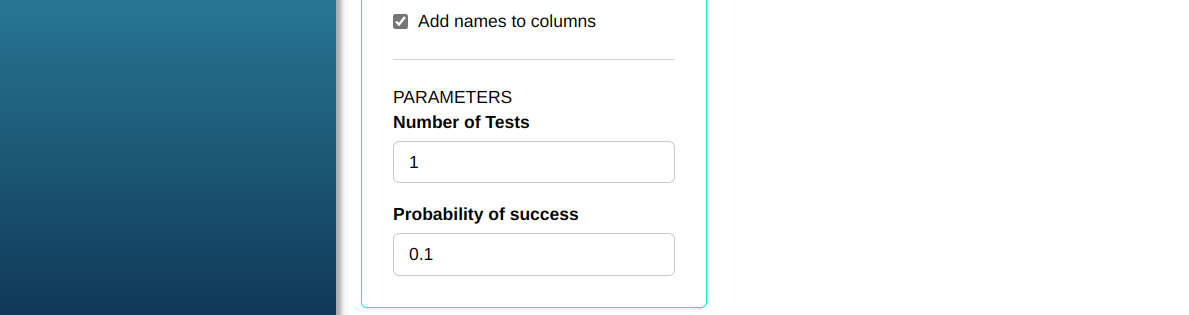
Then click Calculate to get the results. You can also generate the analyses and download them in Word format.

The results are as follows:
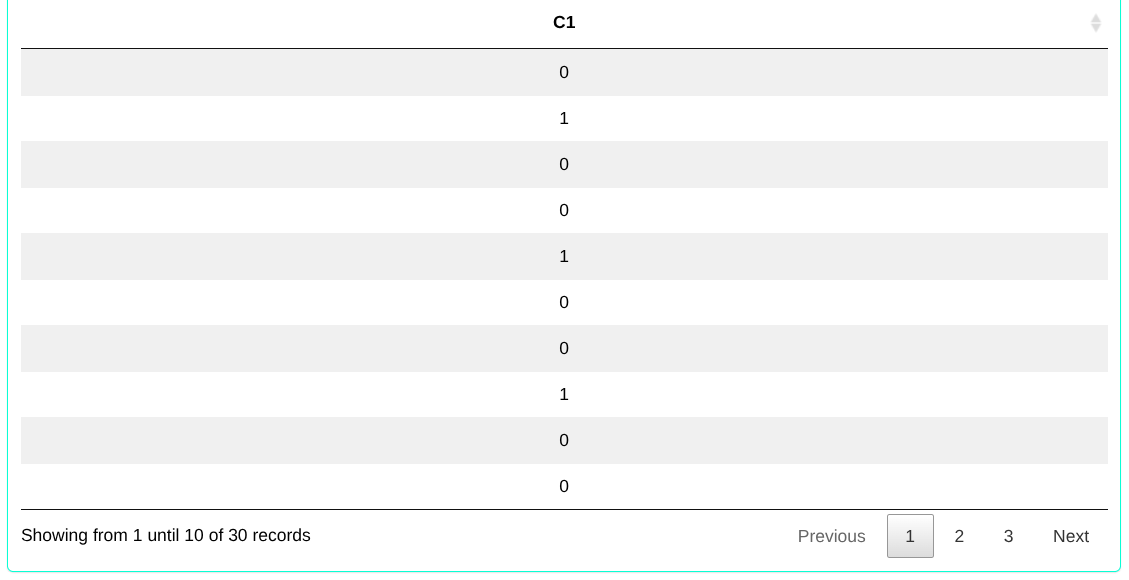
Example 4:
Consider a Poisson-distributed process with a rate of 0.2 defects per unit. Generate five random samples, each with size 30.
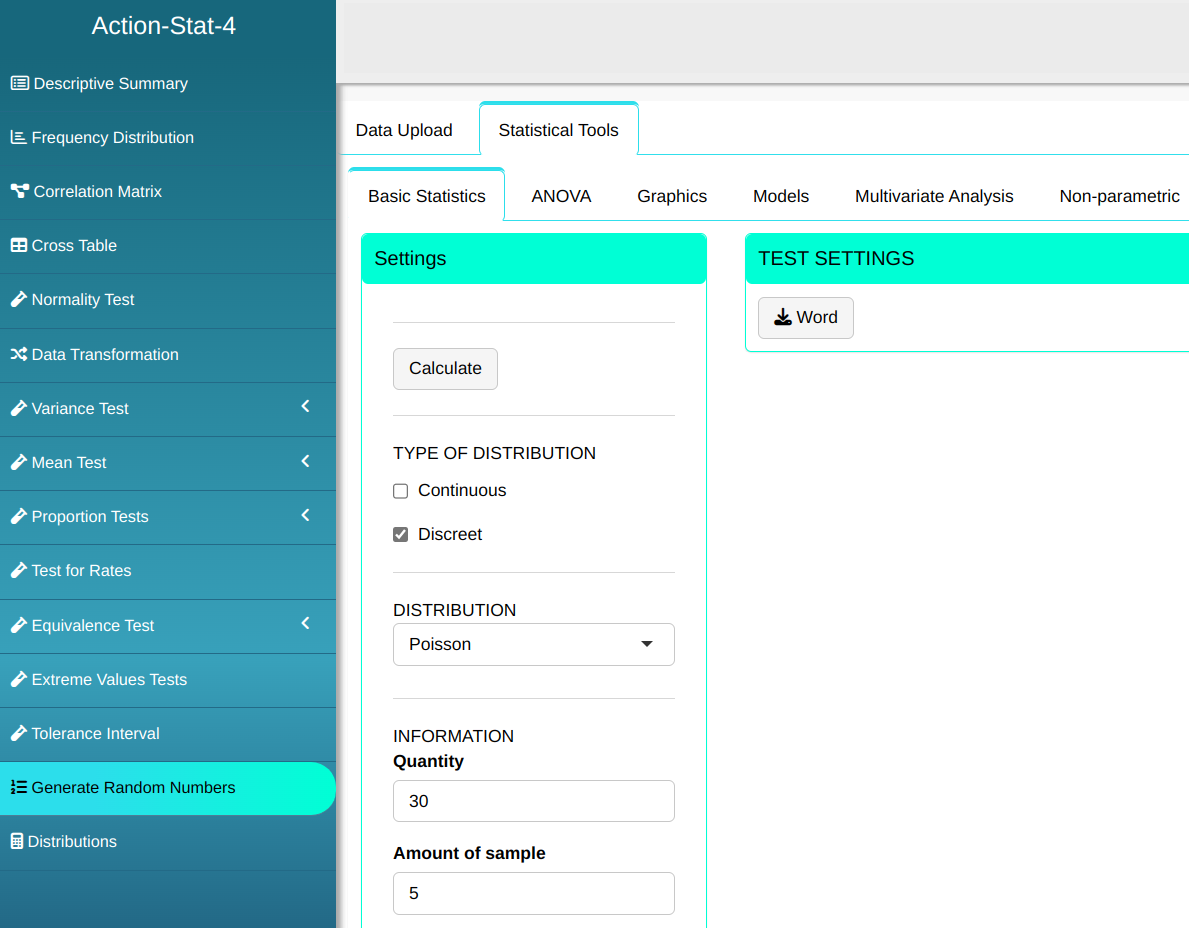
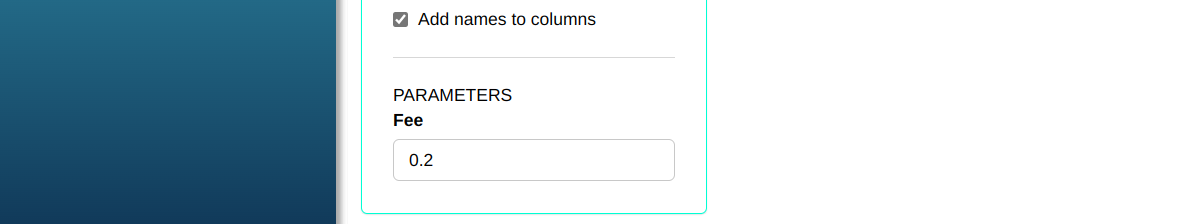
Then click Calculate to get the results. You can also generate the analyses and download them in Word format.

The results are as follows: