7. Microbiological Data
Bacteriostasis and fungistasis tests are carried out to determine microbial count of products.
Example 1:
In a given rinse sampling, a count was carried out of fungi and bacteria, as can be seen in the table below:
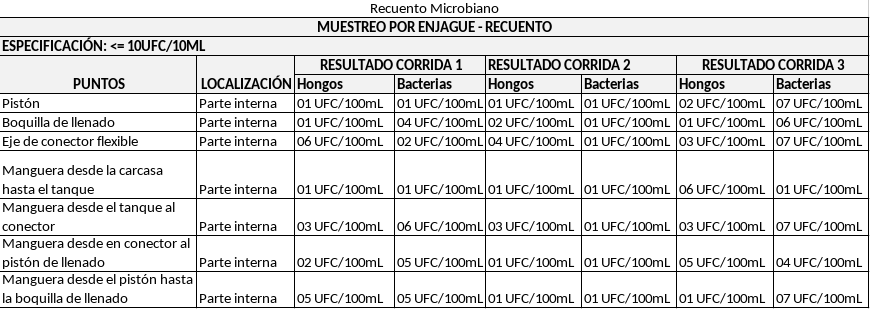
| Bacteria | Sample Size |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 |
| 6 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 7 | 1 |
–
We will upload the data to the system.
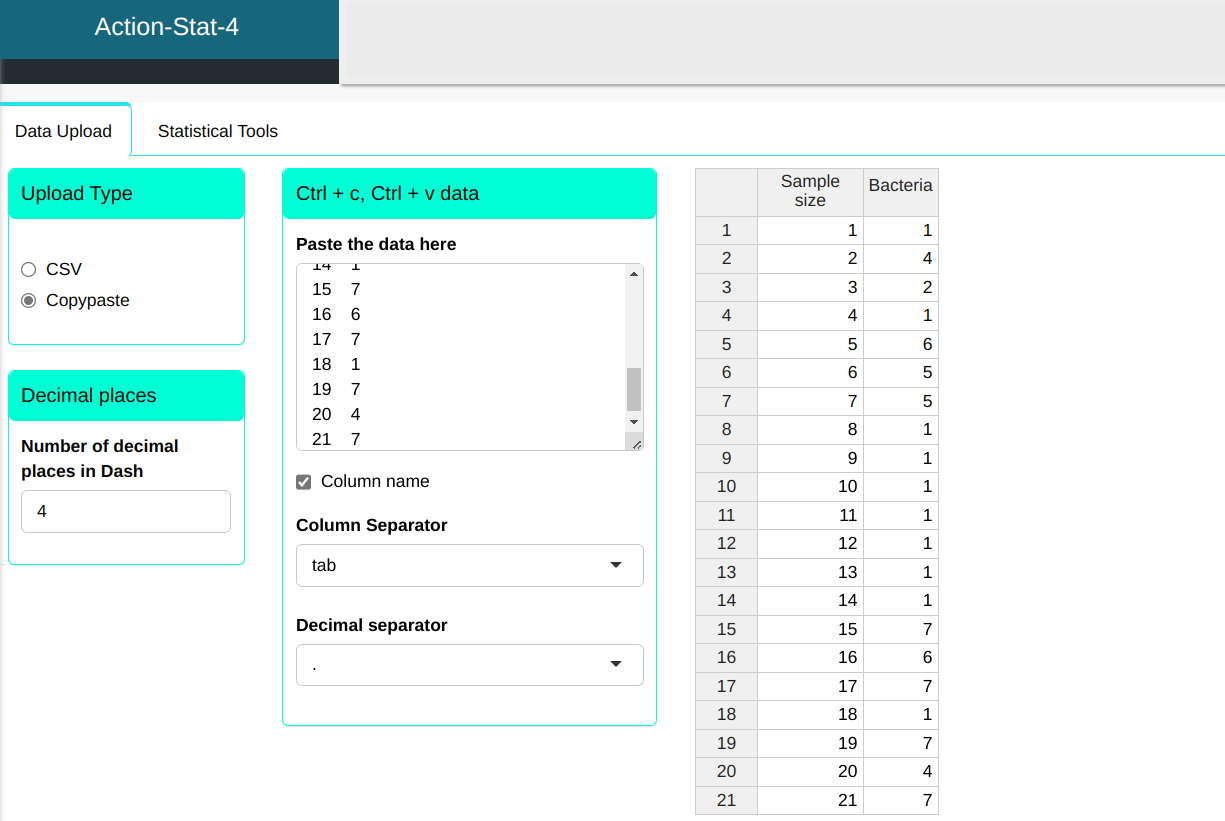
Configure as shown in the figure below to perform the analysis.

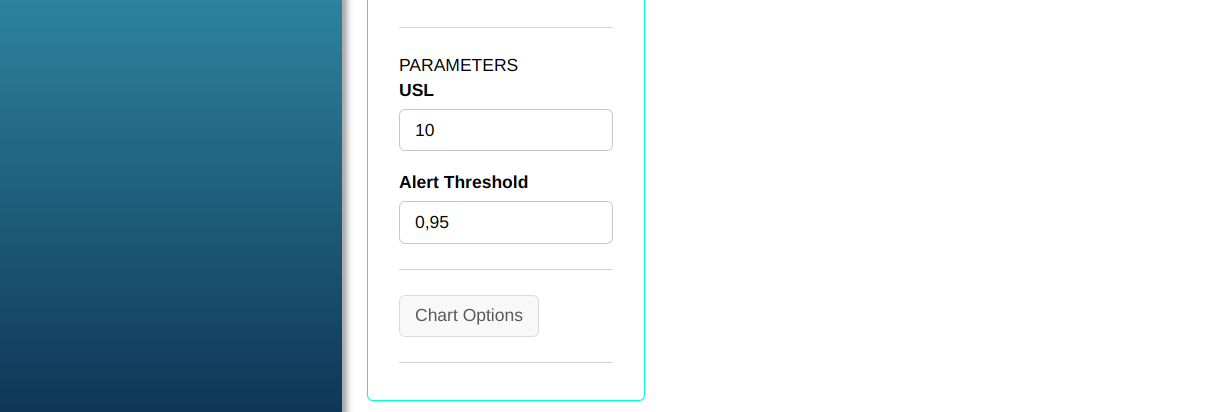
Click on Test Options to decide which tests we are going to execute. In our case, we are going to select all of them, and then click OK.

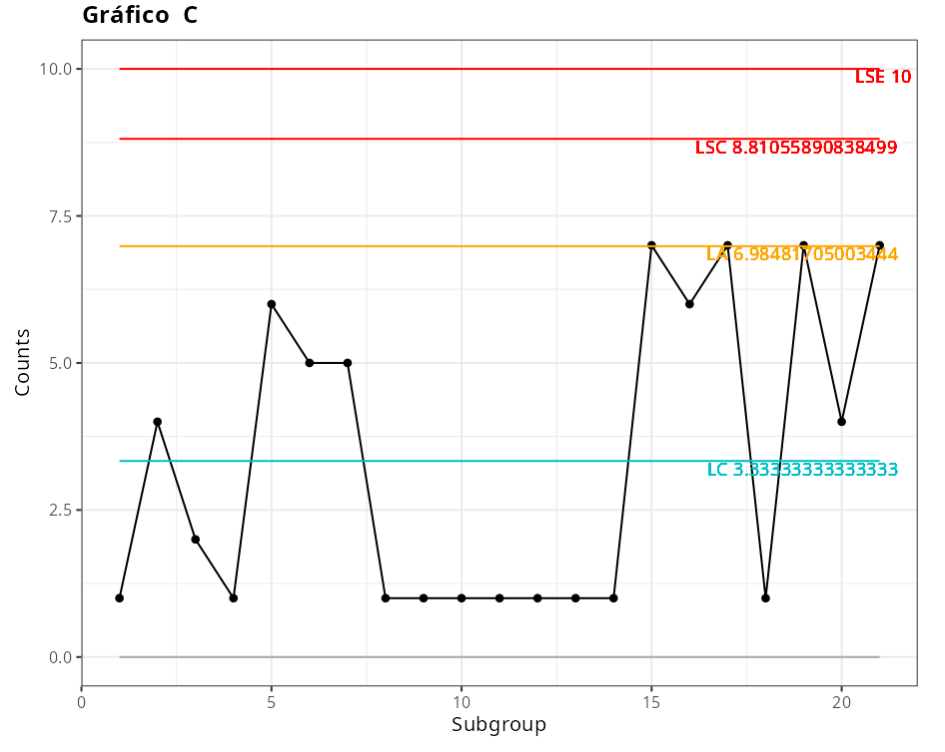
The results are:
SPECIFICATIONS:
| Value | |
|---|---|
| Average Counts | 3.3333 |
| Minimum | 1 |
| Maximum | 7 |
| Alert Threshold | 6.9848 |
| Upper Control Limit | 8.8106 |
| Upper Specification Limit | 10 |
| Probability above LSE | 0.0006915 |
| PPM | 691.5 |
Last modified 19.11.2025: Atualizar Manual (288ad71)