2. Analytical Method
The method analytical for analysis of the measurement system classifies the parts as defective or not. This method compares each part to a specific set and accepts the part if the limits are satisfied, otherwise, it is rejected the piece.
Example:
An attribute measurement device is being used to measure a dimension that has a tolerance of ±0.010. The measuring device is used in automatic 100% end-of-line inspection and is affected by repetitiveness and tendency. To carry out the device study. attribute measurement. 8 pieces with standard measurements in intervals of 0.002 and -0.016 to -0.002 are passed through the measuring device 20 times each.
We will upload the data.
| Piece | Measure | Approval | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -0.016 | 0 | 20 |
| 2 | -0.015 | 1 | 20 |
| 3 | -0.014 | 3 | 20 |
| 4 | -0.013 | 5 | 20 |
| 5 | -0.012 | 8 | 20 |
| 6 | -0.011 | 16 | 20 |
| 7 | -0.0105 | 18 | 20 |
| 8 | -0.01 | 20 | 20 |
| 9 | -0.008 | 20 | 20 |
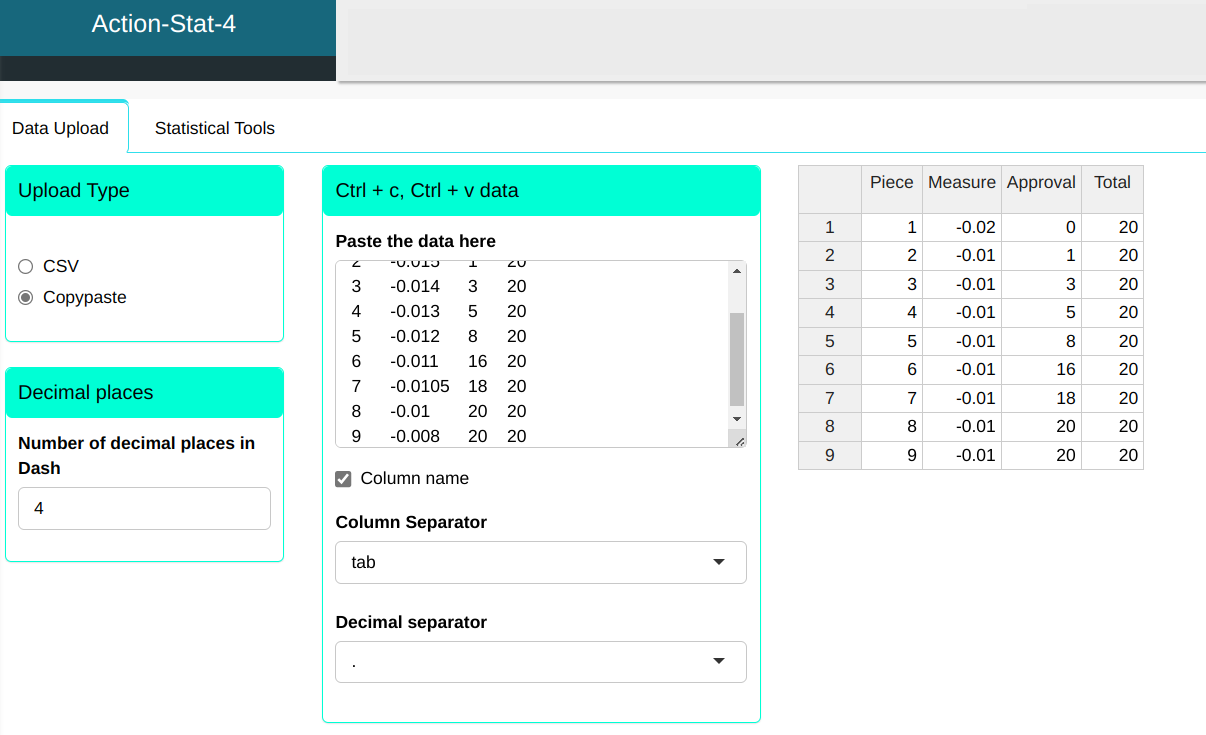
Configuring as shown in the figure below to perform the analysis.

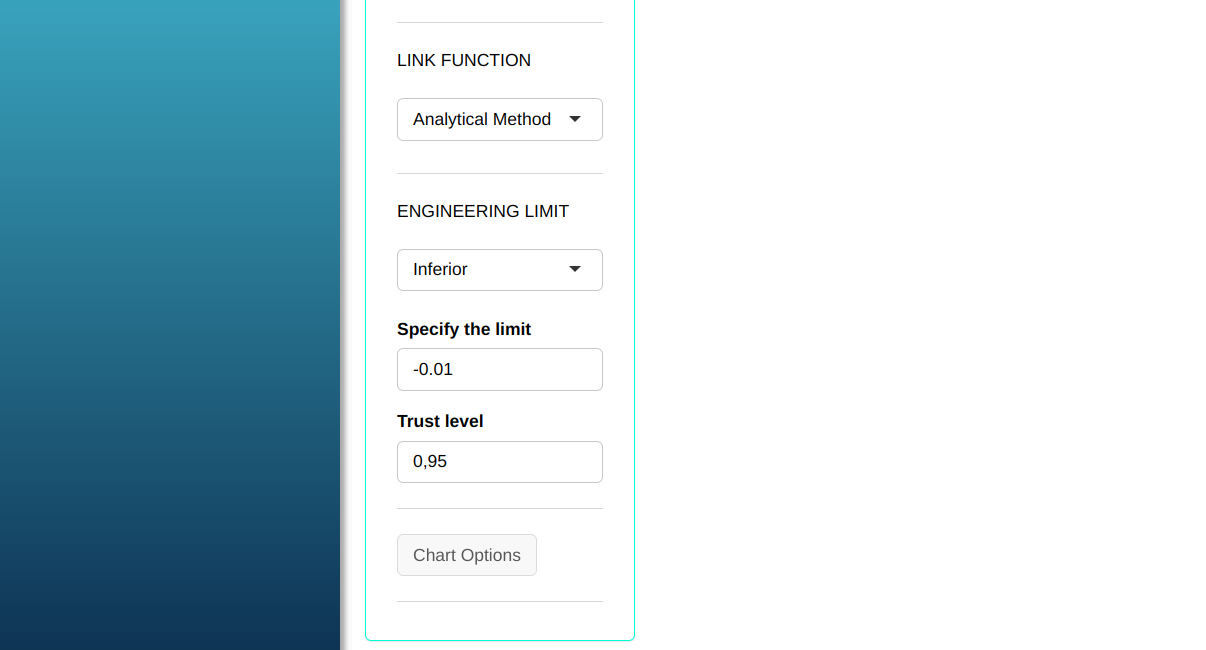
Then click Calculate to get the results. You can also generate the analyses and download them in Word format.

The results are:
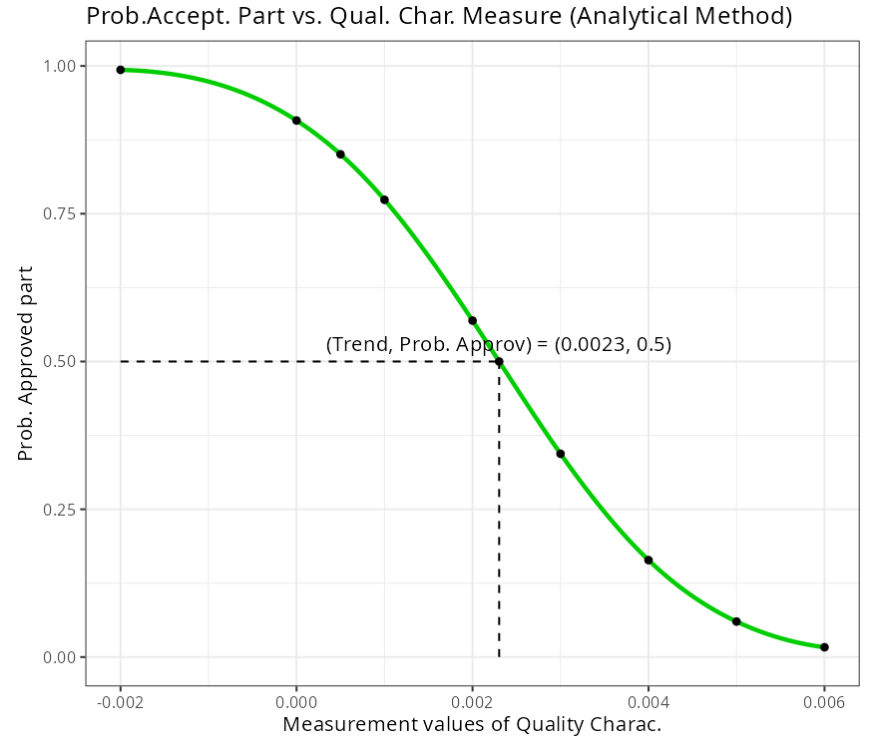
Estimated probability of acceptance
| Xi | Acceptance | Total | pi_i | Phi^{-1} (pi_i) | Prob. Approved part |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.006 | 0 | 20 | 0.025 | -1.960 | 0.0166 |
| 0.005 | 1 | 20 | 0.075 | -1.440 | 0.060 |
| 0.004 | 3 | 20 | 0.175 | -0.935 | 0.164 |
| 0.003 | 5 | 20 | 0.275 | -0.598 | 0.3439 |
| 0.002 | 8 | 20 | 0.425 | -0.189 | 0.5692 |
| 0.0005 | 16 | 20 | 0.775 | 0.755 | 0.7736 |
| 0.001 | 18 | 20 | 0.875 | 1.150 | 0.8505 |
| 0.000 | 20 | 20 | 0.975 | 1.960 | 0.9077 |
| -0.002 | 20 | 20 | 0.999 | 3.090 | 0.9934 |
–
Trend test table
| V1 | |
|---|---|
| Alternative Hypothesis: Mean different from | 0 |
| Trend | 0.0023 |
| Standard Deviation (sigma) | 0.0014 |
| Repeatability | 0.0073 |
| t-statistic | 9.840 |
| P-value | 0 |
| Lower Limit | 0.0023 |
| Upper Limit | 0.0023 |