1. Kruskal-Wallis Test
The Kruskal-Wallis test is a test of hypotheses non-parametric used to compare three or more populations. He is used to test the null hypothesis that all populations have the same function of distribution against the alternative hypothesis that at least two of them have different functions of distribution.
Example:
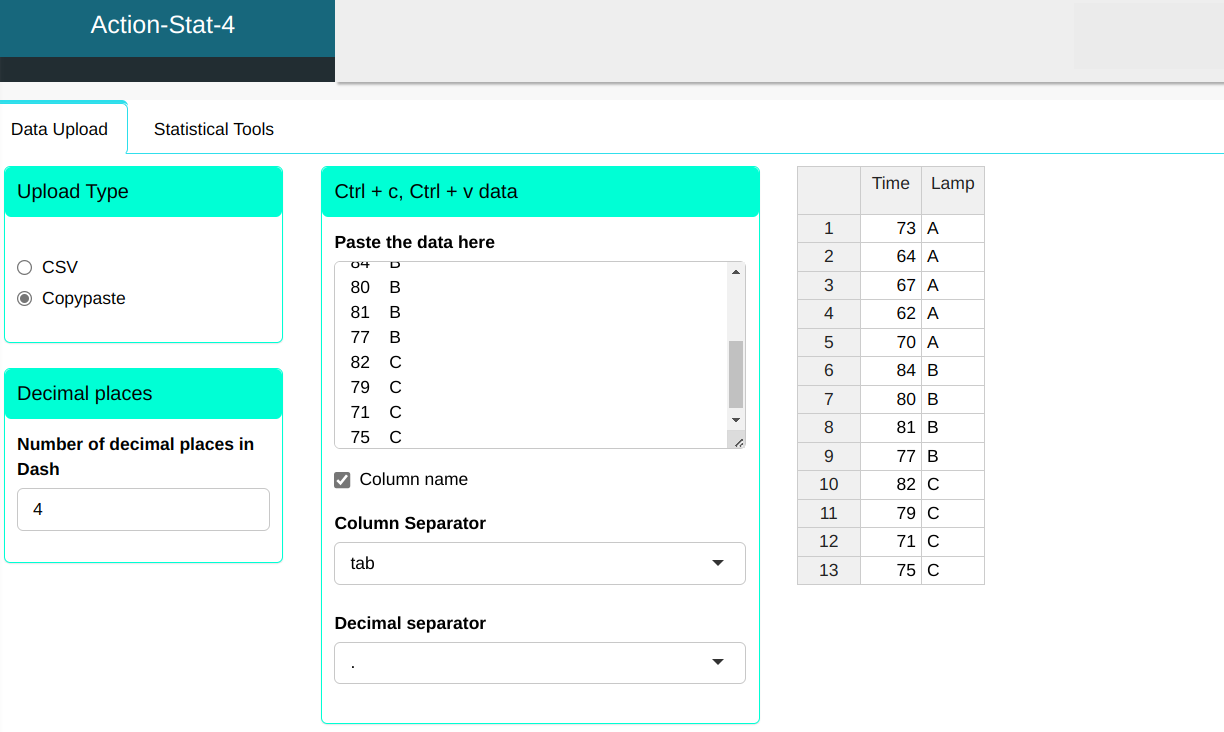
A sample was selected random of three different types of lamps and tested to see how much time the lamps worked. We will upload the results to system.
| Time | Lamp |
|---|---|
| 73 | A |
| 64 | A |
| 67 | A |
| 62 | A |
| 70 | A |
| 84 | B |
| 80 | B |
| 81 | B |
| 77 | B |
| 82 | C |
| 79 | C |
| 71 | C |
| 75 | C |
Configuring as shown in the figure below to perform the Kruskal-Wallis test.
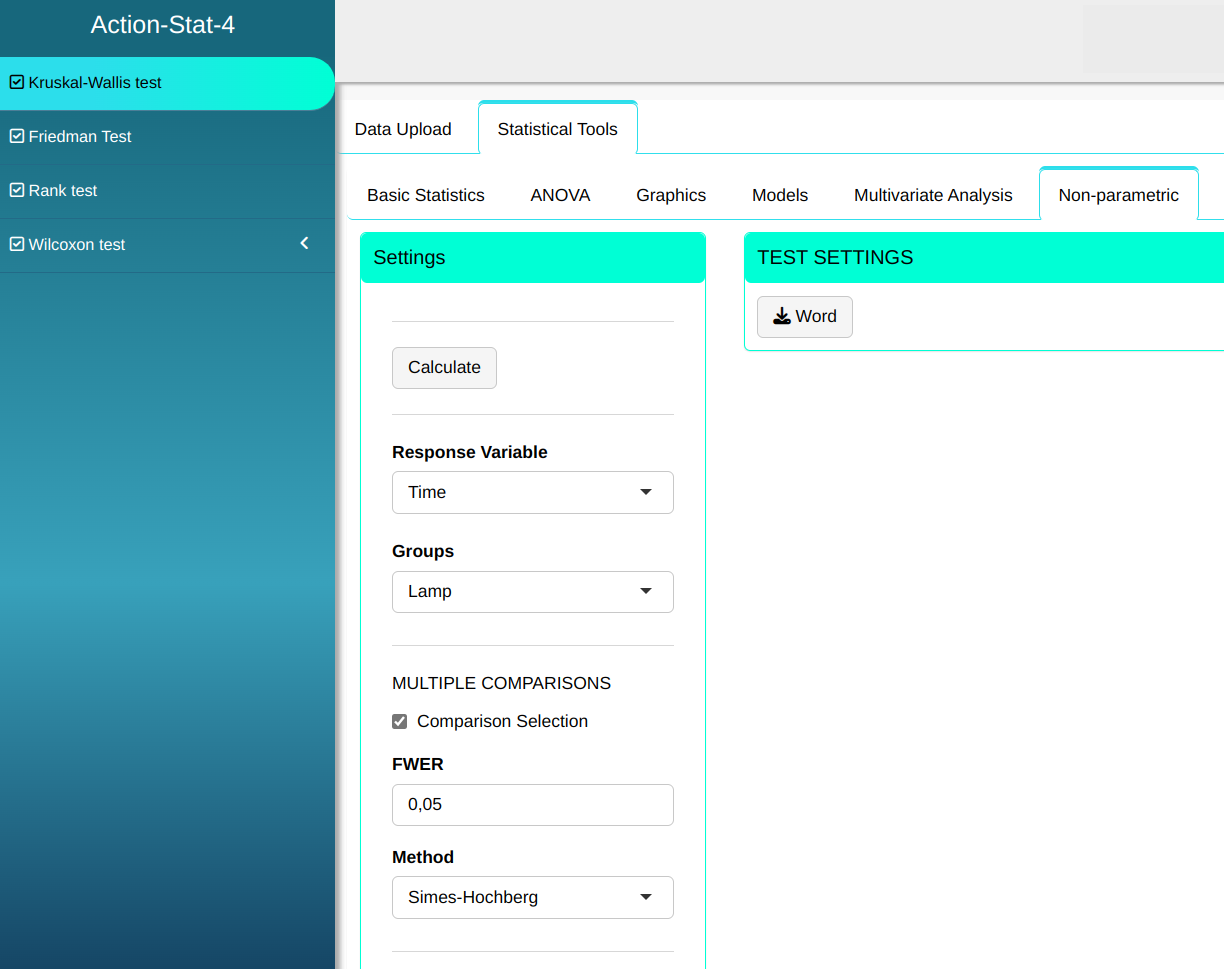
Then click Calculate to get the results. You can also generate the analyses and download them in Word format.

The results are:
Kruskal-Wallis test
| Value | |
|---|---|
| Kruskal-Wallis chi-square test | 8.403 |
| Degrees of Freedom | 2.000 |
| P-value | 0.015 |
Multiple Comparison Table - FWER (Multiple Comparison)
| Observed Difference | Statistics | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Adjusted P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ''A - B '' | -7.30 | 4.659 | -10.791 | -3.809 | 0.003 |
| ''A - C '' | -5.05 | 3.223 | -8.541 | -1.559 | 0.018 |
| ''B - C '' | 2.25 | 1.362 | -1.430 | 5.930 | 0.203 |
Group Table
| Averages (Rank) | Groups | |
|---|---|---|
| B | 10.50 | a |
| C | 8.25 | a |
| A | 3.20 | b |
The test statistic is $\chi^2$=8.4. As P-valor = 0.0149, we reject the null hypothesis that, on average, the three lamps have the same operating time. We therefore conclude that at least one of them has an average operating time different from the too much.
From the Multiple Comparisons table while the operating time of the lamps B and C are similar (P-valor of the compared factor B−C is equal to 0.20297), type A lamps have a shorter operating time than other types of lamps because the compared factors A−B and A−C have P-values 0.0027 and 0.01825 respectively.